Opportunities in Egg Packing: Roles, Skills, and Workplace Insights
Egg packing jobs can offer steady work in various settings, from local farms to large production facilities. This article explores typical responsibilities, skills employers look for, and what to expect in the workplace. Learn how this role fits into the wider food production industry.
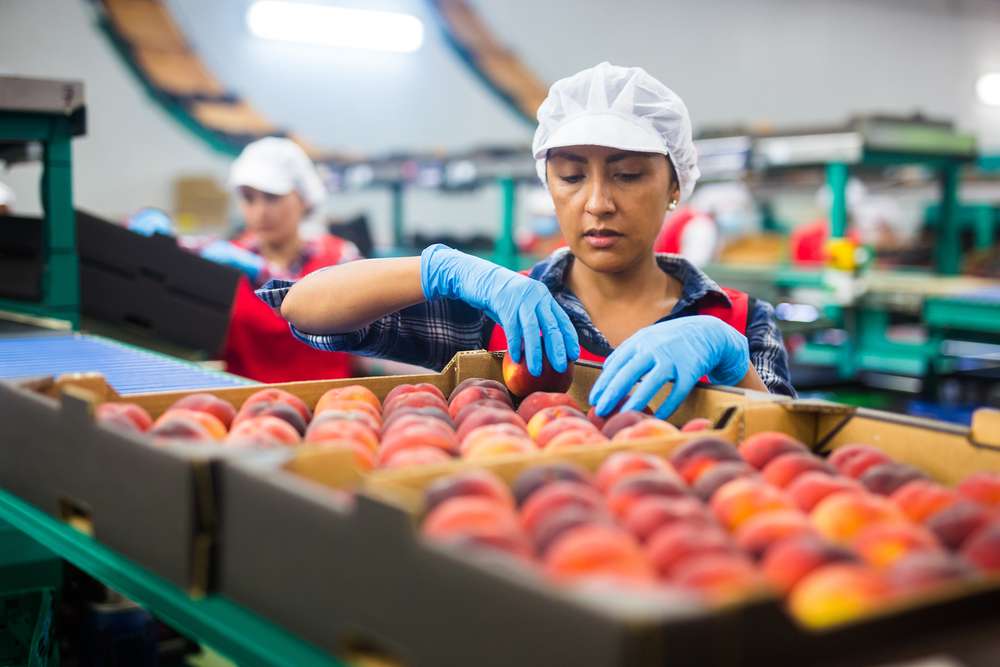

What Are the Main Egg Packing Job Responsibilities?
Egg packing job responsibilities encompass several key tasks that ensure product quality and food safety standards. Workers typically sort eggs by size and grade, removing any damaged or substandard products from the production line. The sorting process requires attention to detail as employees examine each egg for cracks, unusual shapes, or other defects that could affect quality.
Packaging responsibilities include placing eggs into cartons, cases, or specialized containers according to company specifications. Workers must maintain accurate counts and ensure proper labeling with dates, grades, and other required information. Additionally, many positions involve operating or monitoring automated packing equipment, requiring basic mechanical awareness and the ability to identify when machines need adjustment or maintenance.
Record-keeping forms another crucial aspect of these roles, as employees document production numbers, quality issues, and equipment performance. This data helps facilities maintain traceability and meet regulatory requirements for food safety compliance.
Which Skills Are Needed for Egg Packing Roles?
Skills needed for egg packing roles include both physical capabilities and attention to detail. Physical stamina is essential since workers typically stand for extended periods and may lift containers weighing up to 30 pounds. Hand-eye coordination helps with accurate sorting and packaging, while good vision ensures proper quality assessment of products.
Technical skills become increasingly important as facilities modernize their operations. Basic computer literacy helps with data entry and equipment monitoring, while mechanical aptitude proves valuable for operating and troubleshooting packing machinery. Many employers provide on-the-job training for specific equipment and procedures.
Communication skills facilitate teamwork and safety reporting, while reliability and punctuality remain highly valued traits in production environments. Problem-solving abilities help workers identify quality issues and respond appropriately to equipment malfunctions or production challenges.
Understanding the Workplace Environment in Egg Production
The workplace environment in egg production facilities emphasizes cleanliness, temperature control, and efficient workflow. These facilities typically maintain cool temperatures to preserve product freshness, requiring workers to dress appropriately for climate-controlled conditions. Lighting is usually bright to facilitate quality inspection, and floors often feature non-slip surfaces for safety.
Noise levels vary depending on the facility’s automation level, with some environments requiring hearing protection. Work areas are designed for easy cleaning and sanitization, following strict food safety protocols. Production schedules often include early morning shifts to align with egg collection and distribution timelines.
Team-based work structures are common, with employees working in small groups to manage different aspects of the packing process. Supervisors typically provide regular feedback and monitor quality standards throughout shifts. Many facilities promote a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging worker suggestions for process enhancements.
Exploring Career Opportunities in Food Packaging
Career opportunities in food packaging extend well beyond entry-level positions, offering pathways for professional growth within the industry. Starting positions often lead to specialized roles such as quality control inspector, equipment operator, or team leader responsibilities. These advancement opportunities typically come with increased compensation and additional training.
Supervisory positions become available for experienced workers who demonstrate leadership skills and thorough understanding of production processes. Some employees transition into maintenance roles, learning to repair and maintain sophisticated packing equipment. Others may pursue quality assurance careers, requiring additional training in food safety regulations and testing procedures.
The broader food packaging industry offers transferable skills applicable to other agricultural products, processed foods, and beverage packaging operations. Many facilities provide tuition assistance or professional development opportunities for employees seeking additional certifications or education related to food science, logistics, or management.
Maintaining Safety and Hygiene in Egg Packing
Safety and hygiene in egg packing facilities follow strict protocols designed to protect both workers and consumers. Personal protective equipment typically includes hairnets, aprons, and non-slip footwear, with some positions requiring gloves and safety glasses. Hand washing stations are strategically located throughout work areas, with mandatory sanitization procedures before entering production zones.
Training programs cover proper lifting techniques, equipment safety, and emergency procedures. Workers learn to identify potential hazards such as wet floors, equipment malfunctions, or electrical issues. Many facilities conduct regular safety meetings and maintain incident reporting systems to continuously improve workplace conditions.
Food safety protocols include temperature monitoring, pest control awareness, and proper handling procedures to prevent contamination. Workers receive training on Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) principles and may earn certifications in food safety management. Regular facility inspections by both internal quality teams and external regulatory agencies ensure compliance with industry standards.
The egg packing industry provides educational career opportunities with competitive compensation structures. Entry-level positions offer valuable experience in food production and quality control, while advancement pathways exist for motivated individuals seeking long-term career growth. The stable demand for egg products ensures continued employment opportunities in this essential agricultural sector, making it an attractive option for those seeking reliable work in food production environments.